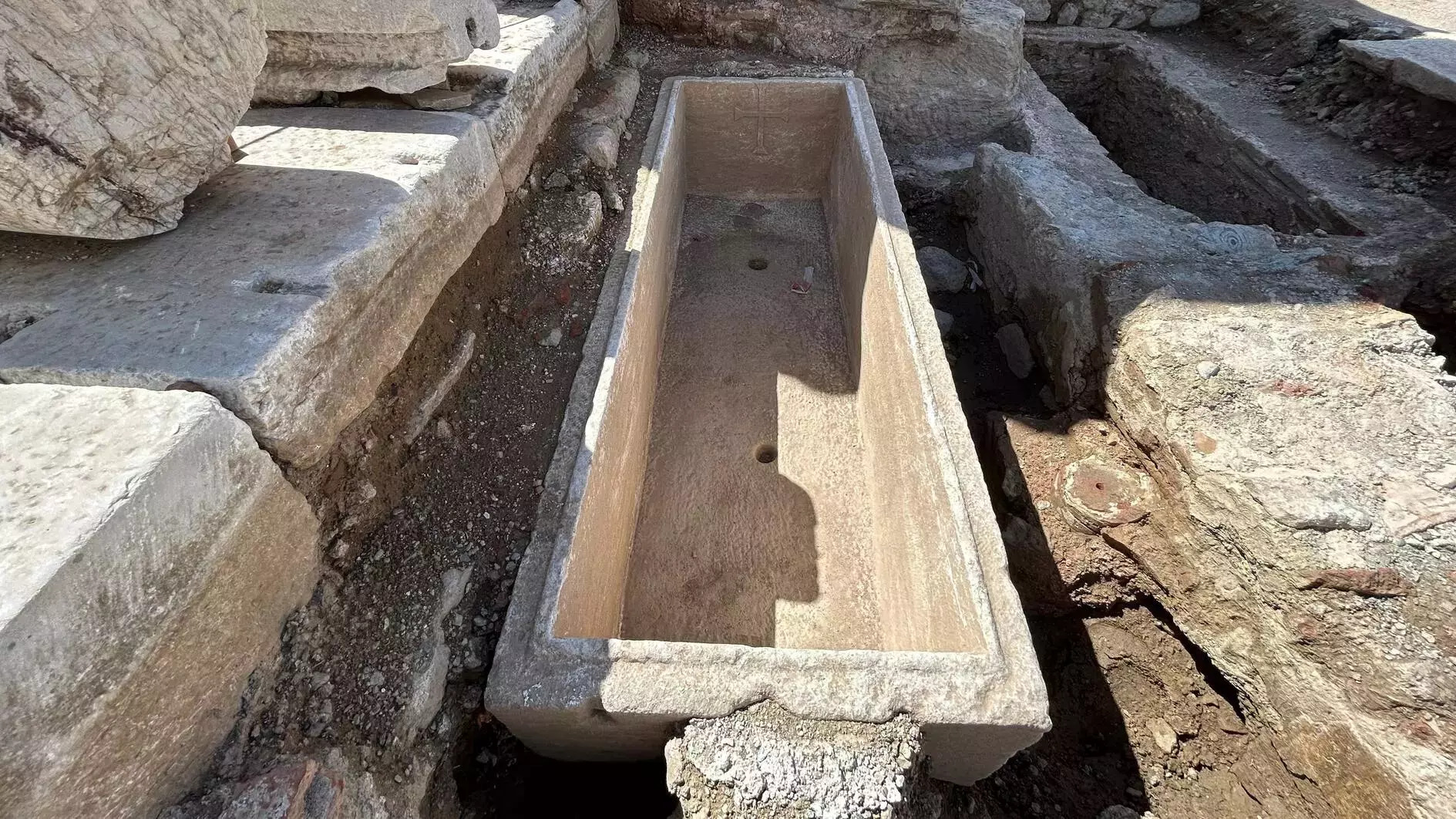
Archaeologists have uncovered a rare sarcophagus, believed to belong to a Roman gladiator named Euphrates, at Ayasuluk Hill in the western province of İzmir. This sarcophagus, dating to the 3rd century B.C., was found containing the remains of 12 individuals, buried in the 5th century A.D.
According to Sinan Mimaroğlu from Hatay Mustafa Kemal University, who is overseeing the excavation, the discovery of the sarcophagus sheds new light on ancient burial practices across centuries.
“There is a beautiful inscription on the sarcophagus indicating it belonged to the Roman gladiator Euphrates,” Mimaroğlu revealed, adding that three crosses had been carved on the inside of the sarcophagus during the 5th century when it was reused for burial. “The fact that this sarcophagus was reused centuries later during the Christian era shows the complex layers of history that exist in the area.”
The excavation team also uncovered traces of a water channel, a funnel system, and mosaics located just beneath the surface.
“We found three sarcophagi and three cross-shaped graves in the area, one of which contained these 12 individuals,” Mimaroğlu said. This discovery points to a mass burial, likely involving upper-class citizens or clergy members, as suggested by the elaborate tomb.
The team has been investigating the Church of St. John in the South Cross branch, which dates to the 5th century A.D. Initial construction began with a modest tomb structure, later expanded into a grand basilica during the reign of Justinian I in the 6th century.
In 2023, Mimaroğlu’s team conducted georadar work in the area, with additional soundings performed by Hörmann. “We excavated a larger area to confirm his data. A marble floor from the early Justinian period was revealed, while the flooring uncovered this year has been shown to belong to the 5th century.”
Mimaroğlu noted that archaeological data proved the mosaic on the lower floor was broken off and placed there in the period after Justinian I.
The sarcophagus was discovered alongside other significant finds, including ceramics from the Early, Middle, and Late Bronze Ages.
With ongoing excavations continuing under Mimaroğlu’s supervision, the team hopes to uncover even more about the rich cultural and historical heritage of Ayasuluk Hill.