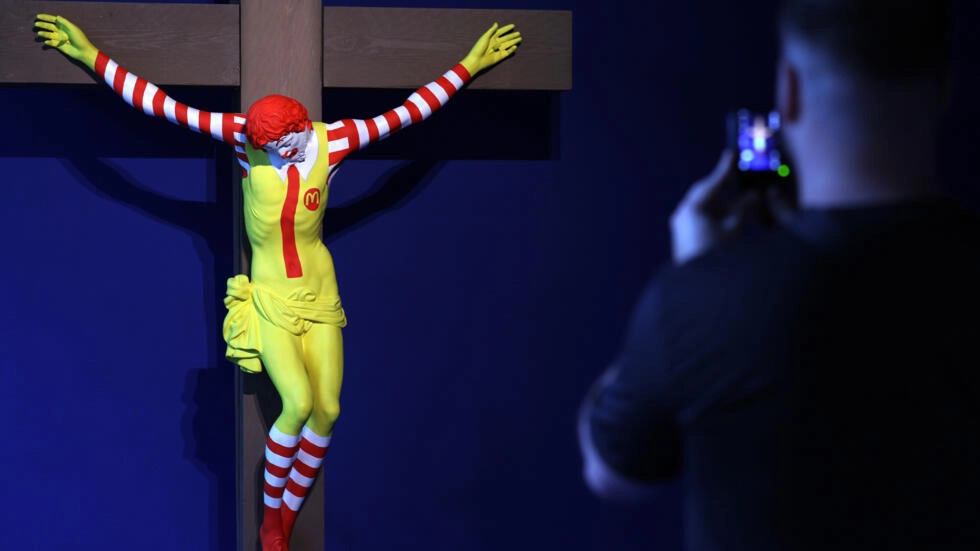
A crucified Ronald McDonald clown, prayer mats adorned with stilettos and sketches by former Guantanamo prisoners take pride of place at a new museum in Spain devoted to previously censored art.
The private Museum of Forbidden Art, which opened to the public in Barcelona last week, features 42 works from around the world that have been denounced, attacked or removed from exhibition.
Works by artists such as Spanish master Francisco de Goya, U.S. cultural icon Andy Warhol and Chinese artist and activist Ai Weiwei are spread over two floors.
The objects are part of a collection of 200 such works belonging to Tatxo Benet, a Catalan businessman.
While they push boundaries and often sparked controversy, Benet said this was not enough to be included in the museum, located in the centre of the Catalan capital, one of the world’s most visited cities.
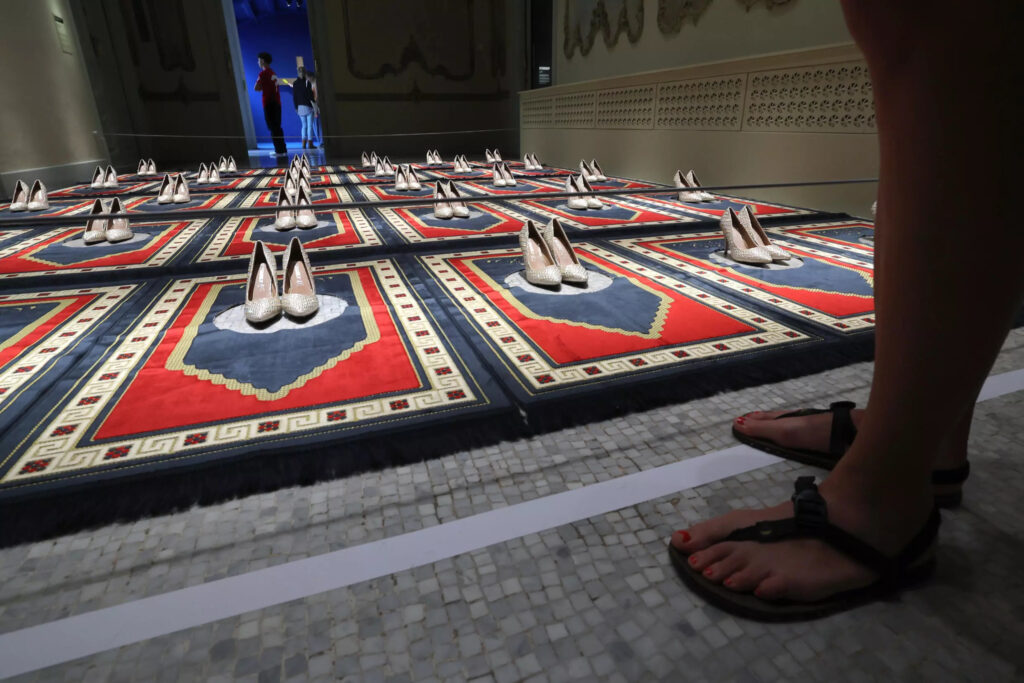

“We don’t collect or show scandalous or controversial works in the museum. We show works in the museum that have been censored, assaulted, violated, banned,” he told AFP.
Many works deal with religion, such as Finnish artist Jani Leinonen’s “McJesus” of a Ronald McDonald sculpture crucified to a wooden cross, which was withdrawn from a museum in Israel.
The museum also showcases a photograph of a crucifix submerged in the urine of New York artist Andres Serrano, which was vandalized during an exhibition in France and sparked an uproar when first shown in the United States in 1989.
Benet, one of the founders of Spanish multimedia group Mediapro, said he started building his collection in 2018 when he bought an installation called “Political Prisoners in Contemporary Spain.”
It consisted of black-and-white photos with pixelated faces of people who had broken the law, among them Catalan separatist leaders who faced legal action over a failed 2017 secession bid.
The work, by Spanish artist Santiago Sierra, was pulled from a Madrid art fair just two hours after Benet bought it. It is now on display at another museum in the Catalan city of Lleida.
The museum also displays paintings and sketches by former prisoners at the U.S. naval base at Guantanamo Bay in Cuba, including one of the Statue of Liberty submerged in water with only the hand holding a torch and top of the crown visible.
The U.S. government ordered that art made by inmates at the detention center would have to be destroyed when they are released after an exhibition of works in New York in 2017 sparked controversy.
“Any artist who can’t show their work because someone prevents them from doing so is an artist who is censored, and therefore will always have a place in this museum,” Benet said.