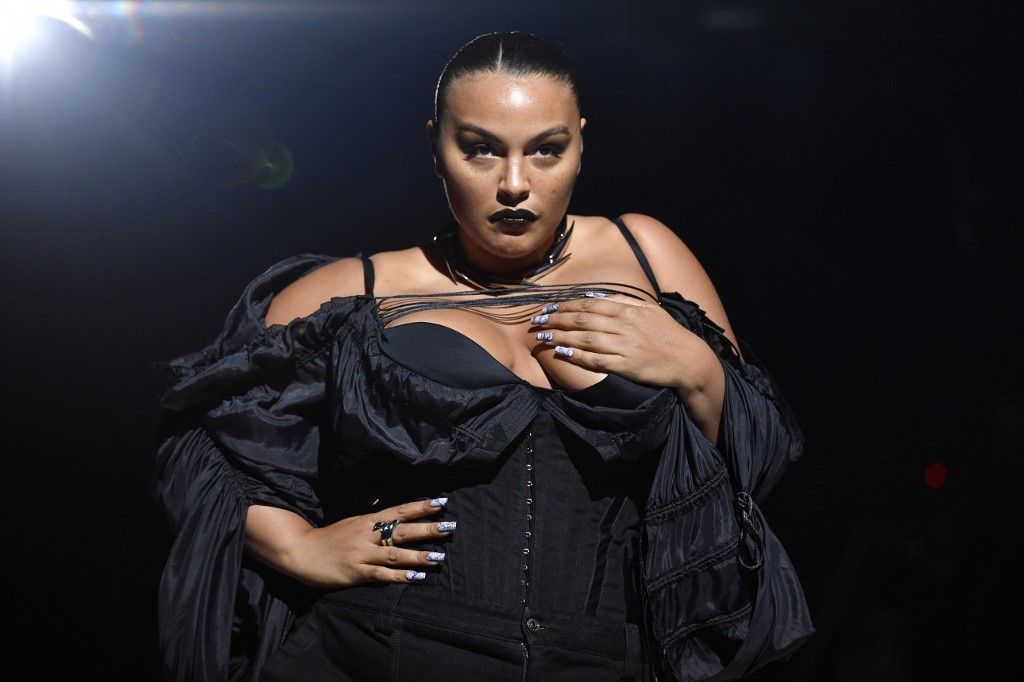
Despite claims that the fashion industry is embracing curvier bodies, the data suggests it could be guilty of what one expert calls “fat-washing.”
While a handful of plus-size models such as Paloma Elsesser have grabbed media attention in recent years, the figures shows they remain a vanishingly small minority.
Vogue Business looked at 9,137 outfits unveiled during 219 shows in New York, London, Milan and Paris last season and found that 0.6 percent were plus-size, defined as U.S. size 14 or above, which is actually the average size for a woman in the United States, and only 3.8 percent were size 6-12.
This means 95.6 percent of outfits presented were in U.S. size 0-4. Paolo Volonte, who teaches sociology of fashion in Milan, says brands use a few curvy models to deflect criticism.
“It’s ‘fat-washing,'” he told AFP, comparing it to criticisms of cynical “green-washing” by which the industry is accused of making empty climate pledges.
“They use curvy models in their shows to show inclusivity but in fact this is to preserve and maintain a system based on the tyranny of the thin ideal,” Volonte said.
Ekaterina Ozhiganova, a 20-year-old model and law student, says luxury brands simply “refuse to represent normal people.”
Medium-sized women “are often told either to lose weight… or to push themselves up to XL,” she told AFP. “Neither is healthy.”
Ozhiganova’s advocacy group, Model Law, carried out a survey that found nine out of 10 models felt pressure to change their bodies, more than half on a regular basis.
“It’s very hard for them to talk about,” she said. “If you complain, everyone will just say: ‘Darling, that’s the job.'” How it became “the job” is a question of history. Volonte says the obsession with thinness dates back to the birth of industrial production techniques.
Ideal image or fat-washing
Previously, designers made clothes specific to individuals. In the mass production era, they use small templates which they scale up for larger sizes. This only works up to a certain size, however, after which fat and muscle can change the shape of bodies in more complex ways.
“It is much more expensive to produce and sell clothing on higher sizes and requires more expertise,” said Volonte.
At the same time, thinness became firmly associated with wealth — having the time and money to work on your body — an aspiration that has been deeply entrenched by advertising and the day-to-day practices of the fashion industry.
There have been efforts to change things since the early 2000s when fears spread that size-zero models were encouraging anorexia in young people.
Since 2017, France requires models to pass medical examinations, while the country’s two biggest luxury conglomerates, LVMH and Kering, signed charters vowing to stop using size-zero models. But with sizes varying from one brand to the next, this is hard to enforce. Designers are as trapped in the status quo as everyone else.
Elite couturier Mohammad Ashi says discrimination based on race and gender has been fairly well tackled in fashion, but shape is tricky.
“We’re not trying to avoid it, but from an industrial point of view, we can’t produce a plus-size dress. We sell what we show and I know our clients personally. It’s just business,” he told AFP.
Couturier Julien Fournie has used pregnant models and his favorite model, Michaela Tomanova, has “six centimeters everywhere more than the others.”
But he says, “fashion remains fashion… It’s a fantasy world and that will never change fundamentally.”